Understanding OrderCloud Assignments
Published by Todd Menier on November 24, 2015
When you save an assignment you are creating a relationship between a party and an object (OrderCloud "thing" such as product, category, etc). For example you might assign a usergroup to a category, thereby granting a user in that group visibility to that category.
There are basic principles around how assignments work that are critical to understanding our data model and more importantly how the data model can be applied to solve the most complex ordering scenarios efficiently.
Assignments are used to define a relationship
Assignments are explicit
Assignments can be made at different levels
Assignments may include configuration data
Assignments cascade down higher levels to the individual user
Assignments are many to many
Assignments are Explicit
When a user is created they exist in a vacuum. The user will not have access to any objects until an assignment is made to them directly, or through a higher level party assignment.
Assignments Can Be Made at Different Levels
Assignments can be made at the company level (buyer, seller, supplier) or any usergroup within one of those companies.
You may notice that some assignments contain configuration options. These options allow you to provide additional information about the assignment. For example, when assigning an address to a user, you can set IsShipping & IsBilling; these properties control whether the address can be used as a shipping and/or billing address on an order.
Assignments Cascade Down Higher Levels to the Individual User
When the API is looking for what a given user has access to, it is checking for assignments. If that user is a member of a party that has an assignment to that object, then that user also has access to that object. Regardless of where an assignment is saved, all of these objects are presented to the user seamlessly and in a very flat structure.
Assignments are Many to Many
Resources can be assigned to many different parties. Those parties can be assigned to many other resources. For example, one user can be assigned to multiple addresses while one address can be assigned to multiple users.
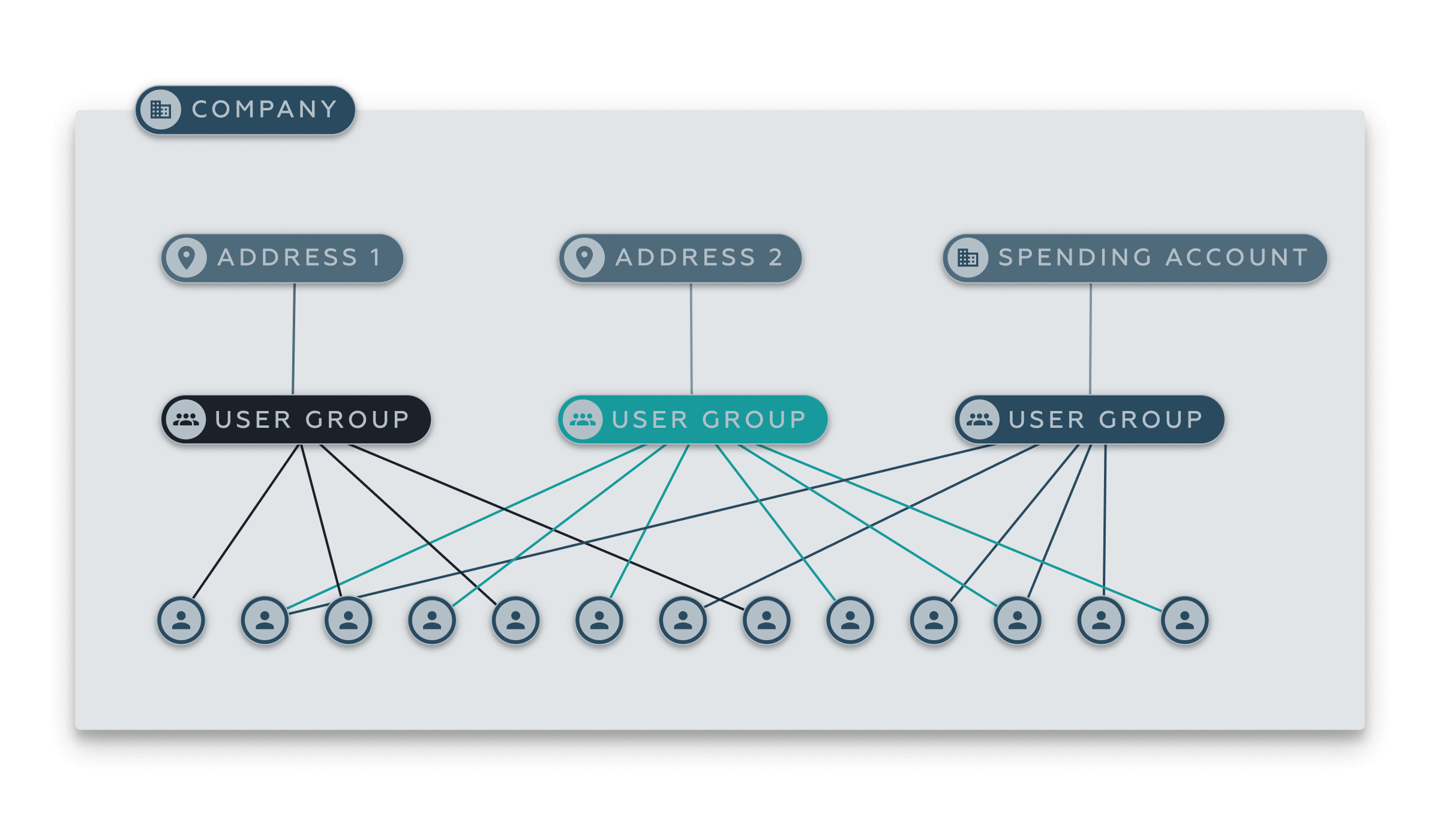
Conclusion
You should now have an understanding of how assignments work from the admin perspective, but generally as an individual user you don't really care about the how or why, you just want to know what you're assigned to. The Me resource which we'll talk about next has the distinct role of rolling up and flattening any assignments to the individual user.
Still have questions?
Ask in our Community Channel